Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the bone tissue and disturbed function of the five lower vertebrae (from 20 to 24). The disease causes discomfort to the patient and is characterized by specific symptoms – pain, stiffness of movement. Osteochondrosis of the back occurs in waves, with periods of exacerbations and remissions. According to statistics, this form is one of the most common. Pathology left unattended often leads to irreversible changes and a significant deterioration in quality of life. However, with a competent integrated approach, osteochondrosis can be successfully treated.
The main causes of pathology
There are no exact data on why degenerative-dystrophic changes are caused in the spine. It is believed that the initial mechanism for the development of the pathology is premature age-related changes in the joints. They can be determined genetically - transmitted by inheritance, but most often initially manifest under the influence of adverse factors.
The main of them is considered to be the improper distribution of the load on the spine. Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine can develop with:
- wearing high heels;
- carrying a bag or backpack on one shoulder without switching.
- sleeping or resting for a long time in an uncomfortable position.
- sedentary work;
- weight lifting.
Those at risk for developing osteochondrosis include the elderly who are characterized by natural destructive changes in cartilage and bone tissue, professional athletes who train daily and intensively, pregnant women, whose center of gravity shifts as the fetus grows and the load on the bottomback increases significantly, office workers are forced to spend a lot of time in a sitting position.
In addition to external risk factors, doctors also call a group of internal ones. These include:
- previous injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
- curvature of the spine;
- flatfeet?
- congenital dislocation or subluxation of the hip joint.
- autoimmune disorders;
- inflammation of synovial tissues;
- pathologies of the circulatory system.
- endocrine diseases?
- portliness.
Osteochondrosis of the lower back can also be caused by toxicosis and prolonged dehydration, bad habits, calcium deficiency and any mechanical effects on the lower back - bruises, bumps, falls.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine: symptoms
The pathology affects not only the bone tissue itself, but also the entire movement part of the spine - vertebrae, intervertebral discs, ligaments, surrounding soft tissues, blood vessels and nerve endings. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine develops, the symptoms of which become apparent with significant damage, gradually and slowly. In the initial stages it is moderate discomfort during exercise, in the latter stages it is acute unbearable pain. Clinical signs are pronounced in the acute stage. During the period of remission, they weaken and in the initial stages this happens even without treatment.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine - symptoms:
- pain in the affected area of the spine.
- pain radiating upwards to the shoulder blades or downwards to the pelvis and hip joints.
- persistent feeling of tension in the lower back;
- difficulty bending and turning the body.
- awkward;
- lameness;
- muscle weakness or, conversely, increased tone.
- tingling sensation.
Not all the described symptoms are always present at the same time. Pain may be associated with limited mobility, but not muscle weakness or numbness. Any of the signs discussed above will be a reason to consult a doctor.
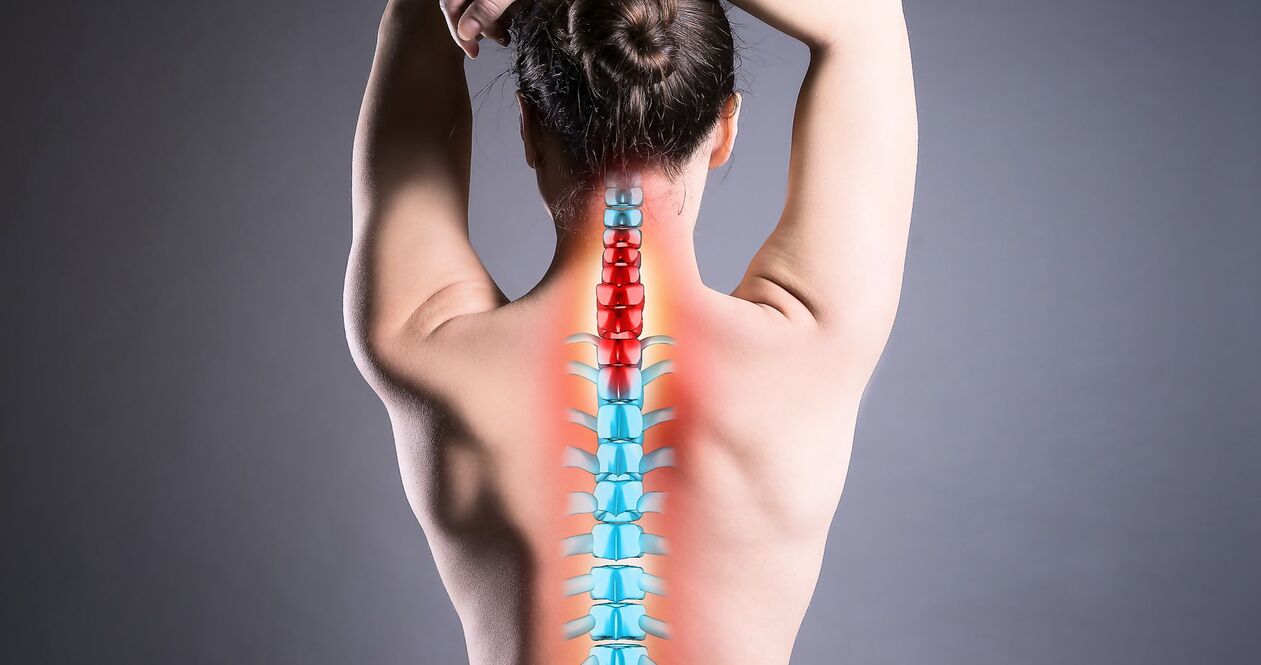
Stages of the disease
The intensity of symptoms accompanying osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine directly depends on the degree of development of the pathology. There are four in total.
- First stage. The first structural and functional changes begin. Intervertebral discs dry out and may crack. Symptoms at this stage are minimal. Many patients confuse it with fatigue after a day's work, wearing uncomfortable shoes or exercising. The main signs of early osteochondrosis are mild discomfort in the lower back, which increases with bending and twisting. It is likely mild pain, which will go away on its own after rest.
- Second stage. The height of the intervertebral discs decreases, the bone structures come closer. This causes a new round of symptoms – stiffness on movement and pain. The pain becomes prolonged and intense and may radiate to the pelvis and legs.
- Third stage. At this stage, the vertebrae are deformed. Protrusions are formed - the intervertebral discs bulge in the region of the spinal canal, but the fibrous rings remain intact. The main symptoms are severe pain, bothersome even at rest, reduced sensitivity, tingling and clicking when moving, tingling and numbness in the lower back.
- Fourth stage. Pathological changes continue to evolve. The functions of the vertebrae are lost. Form of hernia. Osteophytes are formed - bone growths. Blood vessels can be pinched and nerve fibers. As part of the deterioration of blood circulation, the function of the pelvic organs is disturbed. In men, the risk of erectile dysfunction increases, in women, disturbances in the menstrual cycle are observed. Advanced osteochondrosis is manifested by severe lumbar pain in the lower back, lameness, reduced mobility to complete immobility, and increased temperature.
If you are concerned about lumbar osteochondrosis, its treatment will directly depend on the stage at which the disease is diagnosed. In the initial stages, the doctor has in his arsenal many more methods and techniques of rehabilitation. The detection of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the initial stages makes it possible to treat the pathology conservatively, without resorting to surgery.
Forms of pathology
The division into forms is based on the characteristics of the pain syndrome that always accompanies osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine. There are three in total:
- Lumbago. This is a sharp pain that makes movement impossible. The causes of pain can be pinched nerves or muscle spasms.
- Lumbodynia. This is a long, aching pain. It is characteristic of the stage of formation of protrusions and hernias. Also, the discomfort may be related to sprained ligaments.
- Sciatica. This is severe pain that radiates to the pelvic area. The patient complains of pain when walking, sitting or changing body position.
Two more forms of pathology are distinguished according to the accompanying symptoms. The patient may be diagnosed with:
- Root disease. It is accompanied by compression of nerve endings due to deformation of the vertebrae. With this form of the disease, the sensitivity decreases and the affected area becomes numb. Pain and tingling are expressed. Possible decrease in muscle tone, decreased reflexes, tingling in the legs.
- Discogenic lumbar osteochondrosis. This is a serious condition in which the patient is limited in movement. His lower back and extremities are numb. Other symptoms are general weakness, fever, involuntary urination and if the disease is prolonged, weight loss.
Risk of spinal disease
If not treated, osteochondrosis is fraught not only with unbearable pain and stiffness of movement, but also with a number of pathologies that can develop against its background. The most common complications:
- intervertebral hernia;
- inflammation of the sciatic nerve;
- radiculitis?
- partial paralysis.
In order to avoid the accompanying pathologies, it is necessary to start the treatment of osteochondrosis immediately from the moment of detection. With a competent approach to treatment, it is possible to stop or significantly slow down the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine must be differentiated from other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, which may present with similar symptoms. The primary stage is consultation with a neurologist, orthopedist or surgeon. The doctor clarifies complaints, collects memories, conducts a physical examination, paying attention to the characteristics of the patient's posture and posture, the nature of his work activity, bad habits and concomitant diseases.
For the most accurate diagnosis, organic techniques are used:
- MRI?
- x-ray?
- myelography with contrast.
- multislice computed tomography.
Each of the diagnostic procedures allows the doctor to assess the condition of the lumbar and sacral spine at the current moment. The images clearly show structural changes in the vertebrae, indicating the stage of osteochondrosis. Based on the data obtained, the specialist decides on the tactics for the further management of the patient.
Laboratory diagnosis is not critical, however, studies may be recommended if indicated. In particular, if lumbar osteochondrosis is diagnosed, treatment may be prescribed based on blood test results. They are necessary to clarify the intensity of inflammatory processes in the muscle fibers adjacent to the spine.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: treatment
The fight against pathology is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist and begins after a comprehensive diagnosis, when the degree and extent of tissue damage is determined. Modern medicine offers a number of effective conservative methods. If their use does not lead to the expected result, doctors resort to surgery.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: treatment with physical therapy methods
All physical therapy techniques are good because they affect the sacral and lumbar spine in a comprehensive way. This approach allows you to deal with pain, reduce inflammation and restore normal blood circulation.
When osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine progresses, treatment must be comprehensive. Patients with complaints are prescribed:
- electrophoresis - exposure of the problem area to continuous electrical pulses with the possibility of using drugs for external use.
- transdynamic therapy - a variant of electrotherapy that uses pulsed currents.
- magnetotherapy - treatment with alternating or static magnetic fields.
- ultrasound therapy - the effect of high-frequency sound waves.
- shock wave therapy - exposure to low frequency acoustic impulses.
It is important to consider two nuances. Firstly, the effect of physiotherapy treatment is noticeable only after a course of procedures, the duration of which is selected individually for each patient. The second is that physiotherapy as an independent method works for early grade osteochondrosis. For large-scale lesions, it is recommended as an adjunctive technique in addition to medical and surgical treatment.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: treatment with drugs
Pharmacotherapy for injuries of the lumbar and sacral spine is aimed at relieving acute pain and suppressing inflammatory processes. The method is relevant in the acute stage, when symptoms interfere with full life.
How to treat lumbar osteochondrosis with drugs is always decided individually. A neurologist can prescribe drugs from different pharmacological groups. Basic:
- NSAIDs (systemic and local) to suppress inflammation in the vertebrae and adjacent tissues.
- muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms.
- Vasoprotectants to improve blood circulation.
- chondroprotectants to protect the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs from destruction.
- B vitamins to improve nerve conduction.
- pain relievers for sharp pains that limit mobility.
Exercise therapy as a treatment method for the pathology of the sacral and lumbar regions
Intense training for osteochondrosis is strictly prohibited, but you cannot completely give up physical activity. Conversely, exercises of moderate strength and duration help to restore blood circulation and reduce pain.
How to treat osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine with exercise therapy:
- Exercise with an instructor. The instructor will show you which exercises are allowed in a particular situation and make sure they are performed correctly. Even the smallest flaws in technology can significantly reduce the effectiveness of training or even cause harm.
- Prepare carefully for the lesson. Before exercise, it is recommended to warm up the muscles - you can gently massage the lower back and the sacrum.
- Dose the load strictly. The lower back is a vulnerable area. To avoid overtraining, you need to monitor the duration of the lessons. Their optimal duration is no longer than 20 minutes.
- Gradually increase the intensity of the exercise. For beginners without experience, simple exercises and short programs are suitable. For those who have already been doing exercise therapy for some time, you can move on to more complex options.
- Remember to be regular. A one-time workout will not bring visible improvements. Pain in the lumbar and sacral spine is reduced if the patient participates in exercise therapy on a regular basis - ideally twice a week.
- Consider the contraindications. Physical therapy has been shown to be a safe method for treating osteochondrosis, but there are limitations. You should stop exercising if you feel unwell: fever, weakness or a rise in temperature.
Lumbar osteochondrosis, the treatment of which should take into account the period of the disease, will not bother you if all the rules are strictly followed.
- In the acute period. Only smooth and slow movements are allowed. If the pain increases during exercise, you should stop and rest your joints.
- In the subacute period. The pain syndrome subsides, mobility is restored, so you can slightly increase the intensity of training and increase its duration. But, to avoid aggravation, you need to carefully monitor your well-being.
- In recession. We allow the whole range of exercises for pathologies of the lumbar spine, but it is important to remember that overuse is fraught with a new exacerbation of the disease.
If lumbar osteochondrosis is diagnosed with mild or moderate severity, treatment with physical therapy can also be carried out at home. After perfecting the exercise technique under the supervision of an instructor, repeating the exercises at home is not prohibited. For training you will need an exercise mat, a roller and a ball.
Modern exercise therapy and rehabilitation rooms are equipped not only with traditional accessories, but also with special medical simulators. They help you recover from illness gently and safely, and also make activities more fun and interactive. For example, the neuromuscular recovery system turns recovery into an exciting competition with oneself. The patient stands on a moving platform and performs the exercises presented on the screen. Another important advantage of the simulator is the ability to monitor even the slightest progress in the patient's condition. The system evaluates the result of each exercise performed and the doctor can see the progress from workout to workout. Knowing one's success also motivates patients to try harder and not give up.

Manual therapy
Good results can be achieved if you supplement exercise therapy and medication for lumbar pathology with manual therapy. The method allows:
- elimination of hypertonicity of muscle fibers.
- relieve pain;
- restoration of blood supply to the lumbar and sacral region.
- improving the course of metabolic processes.
Manual therapy is an effective way to properly redistribute the load on the spine and protect yourself from further destructive changes. The good thing about this method is that it not only relieves pain, but also prevents neurological disorders that often develop against the background of lumbar osteochondrosis.
Currently, chiropractors combine massage and physical therapy methods, such as tecartherapy. Electromagnetic waves penetrate deep bone tissue and allow you to relieve pain attacks and quickly restore mobility.
Surgical methods
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the treatment of which with drugs, physiotherapy and exercise therapy is not always effective, significantly complicates the patient's life. In some cases, only surgery is applicable to eliminate pain and restore back mobility. Modern methods and technological equipment make it possible to perform minimally invasive operations with a shortened recovery period.
For osteochondrosis, the following methods of intervention are relevant:
- endoscopic resection of the intervertebral hernia - using microsurgical instruments and a built-in camera.
- removal of intervertebral disc herniation - using neurosurgical tube dilators.
- laminectomy - surgical removal of pathologically changed bone processes.
- microdiscectomy – elimination of the hernial protrusion.
Immediate indications for surgery are recurrent hernias, spinal stenosis, when the spinal canal narrows, and degenerative spondylolisthesis, a condition in which the vertebrae shift from one another. In all other cases, if osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is confirmed, doctors try to carry out treatment using conservative methods.
Disease prevention
The symptoms of osteochondrosis cause suffering, and the treatment of the pathology can take a long time. It is much more effective to protect the vulnerable lumbar region from overexertion in advance. For preventive reasons it is recommended:
- Properly organize your workplace during office work. The back of the chair should support the lower back and the table should be of appropriate height.
- Avoid uncomfortable shoes. The optimal heel height for women is up to 5 cm. It is also recommended to exclude flat soles, as they contribute to foot deformity and flat feet - one of the factors.
- risk of osteochondrosis.
- Exercise. Lifting heavy objects should be avoided. Swimming, walking and cardio training are useful if there are no contraindications.
- Eat a balanced diet. The diet should contain foods that are sources of calcium, phosphorus and B vitamins. These are fish, dairy products, leafy vegetables and grains. These substances are needed to strengthen all the elements of the joints and support the nervous system.
- Make sure you get enough sleep. It is better to sleep on an orthopedic mattress of medium hardness. It will provide an anatomically correct posture in which the body rests from everyday stress.
- Check body weight. Obesity is one of the causative factors. If the weight is normal, the load on the spine will be adequately distributed and the risk of circulatory disorders will be minimized.
The prognosis for patients with osteochondrosis directly depends on the degree of damage to the vertebrae. That is why early diagnosis is extremely important. If you are worried about lower back pain and the images reveal destructive processes in the initial stages, you need to start treatment. In the early stages, drugs and physical therapy are effective. In later cases, it is rarely possible to do without surgery. Exercise therapy can be used as an additional measure of help in any form and at any stage.